Cavities: Complete Guide to Understanding, Preventing, and Treating Tooth Decay

By the age of their mid-30s, more than 80 percent of the Americans have at least one cavity. Holes are minute gaps that open in your teeth as a result of acid erosion that destroys your tooth enamel. These are some of the prevalent chronical diseases in the United States. If you need more interested info like that visit quick guider.
The cavities are an important aspect of oral health. The more immediate your treatment of a cavity, the higher there is likelihood of good results. This is the guide that will teach you all that you need to know about tooth decay, beginning with early indication up to treatment procedures.
What Are Cavities? Understanding Tooth Decay Basics
Cavities Definition and Formation Process
Cavity is a gouge in your tooth, which is formed under the influence of tooth decay. Acids in your mouth cause holes in your teeth which form the cavities. The outer layer of your teeth is hard and it is referred to as your tooth enamel.
Here’s how cavities develop:
Foods and beverages that contain sugar are consumed by bacteria of your mouth such as fruit, candy, bread, cereal, sodas, juice and milk. These microbes break down carbohydrates to acid. Dental plaque is formed as a result of the mix of the bacteria, the acid, the foodstuff, and the saliva. This is a sticky substance that is on your teeth.
Unless you brush your teeth and floss every day, the acids contained in plaque break down the enamel in your teeth. This will give holes into your tooth enamel surface. If you want to read about Hemorrhoids: Complete Guide to Symptoms, Treatment, and Prevention.
Different Names for Cavities
Cavities have several names that mean the same thing:
- Dental caries
- Tooth decay
- Tooth cavities
All these terms describe the same condition where your teeth develop holes from acid damage.
Types of Cavities: Where Tooth Decay Occurs
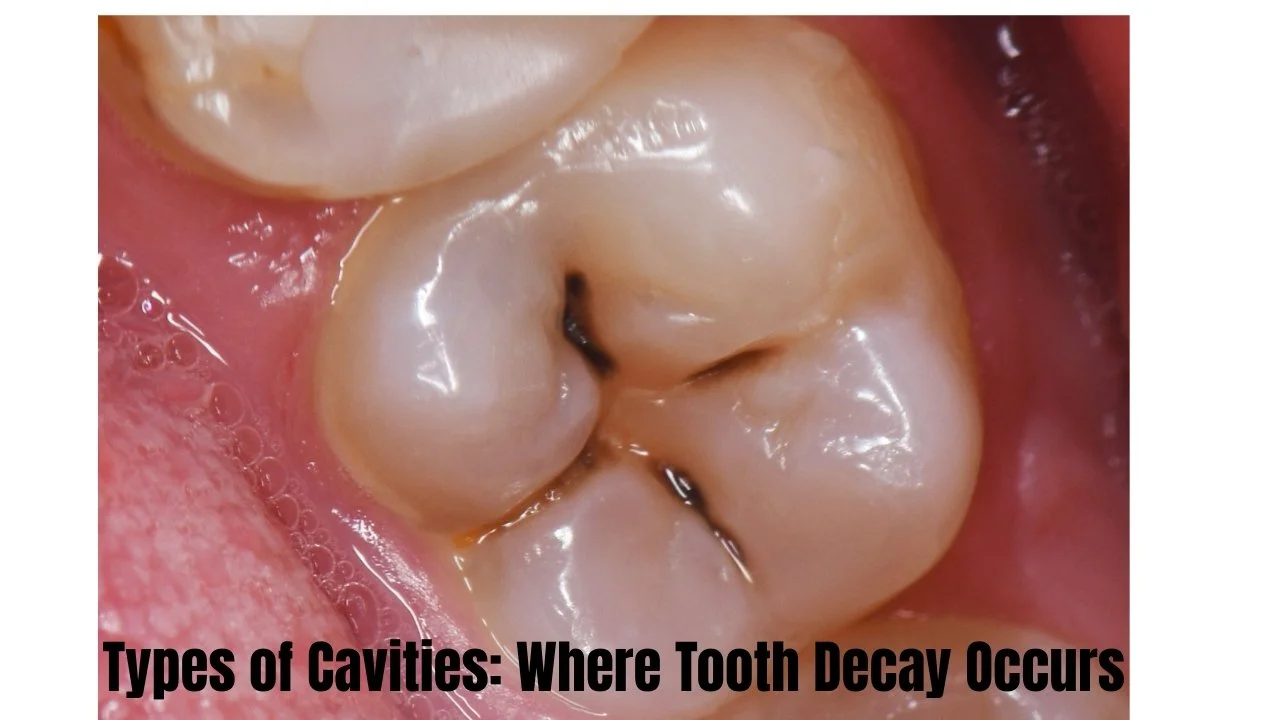
Smooth Surface Cavities
Smooth surface cavities refer to slow growing cavity that dissolves tooth enamel. They can be avoided by good oral hygiene. Individuals between the age of 20-29 tend to develop this form of tooth decay among their teeth.
These cavities commence small and develop at a slow pace. Properly maintained, it may even be possible to remineralize early smooth surfaces cavities.
Pit and Fissure Decay
Pit and fissure decay develops on the upper surface of the tooth which is used in chewing food. This kind of cavity takes place in the anterior side of your back teeth as well. The pit and fissure decay are likely to begin in the teenage years and increase rapidly.
Bacteria and food get stuck in the grooves and pits of the food surfaces that you chew on. This causes such areas to be difficult to clean and become more susceptible to formation of cavities.
Root Decay in Adults
Root decay can easily be experienced by adults with receding gums. Tooth root exposure to dental plaque and acid is caused by gum recession. Root decay is more difficult to prevent and treat as compared to other cavities.
When you have receding gums, consult your dentist as to whether you should consult a periodontist or not. A periodontist is an expert who treats periodontal disease and periodontal recession.
Cavity Statistics: How Common Are Cavities in America?
Cavities are very widespread in the United States. Over 80 per cent of Americans possess at least one cavity before the age of 35. Tooth decay is among the widely prevalent chronic illnesses that affect individuals at any age.
The cavities may occur at any age. The presence of tooth cavities is more prevalent amongst children, however. A lot of children do not brush adequately and frequently. Children also consume more sugary food and beverages as compared to adults.
Cavities are also common among many adults. New tooth cavities may sometimes form around the periphery of childhood-treated cavities. Receding of the gums in adults is also higher, thereby exposing roots of the teeth to accumulation of plaque.
Who Gets Cavities? Risk Factors and Demographics
Cavities in Children vs. Adults
The decay of teeth may occur at any age, though cavities are more frequent in children. Children do not brush well or on a regular basis. They also take more sugary foods and beverages as compared to adults.
The teeth of children are also younger and they might not be fully safeguarded by fluoride. Their nutrition such as eating in between meals makes them more exposed to cavities.
High-Risk Groups for Tooth Decay
Certain factors increase your risk of cavities:
Dry mouth (xerostomia) from conditions like Sjögren’s syndrome
Taking medications like antidepressants that cause dry mouth
Family history of tooth decay
Gum recession that exposes tooth roots
Previous radiation therapy for head and neck cancer
Eating sugary foods and drinks often
Poor oral hygiene habits
Cavity Symptoms: Recognizing Signs of Tooth Decay
Early Stage Cavity Symptoms
In most cases, tooth decay on the outer tooth enamel would not present any pain or symptoms. The symptoms are more likely to be observed when there is decay through the enamel into the dentin and pulp.
Early signs of cavities include:
- Small white chalky spots on teeth
- No pain or discomfort
- Spots that may be hard to see
Advanced Cavity Warning Signs
As cavities get worse, you may experience:
Bad smelling breath, bad taste in mouth.
Facial swelling
Toothache or mouth pain
Sensitive to hot, cold or sweet food and beverages.
Brown or black spots on teeth
The 5 Stages of Tooth Decay: From Demineralization to Infection
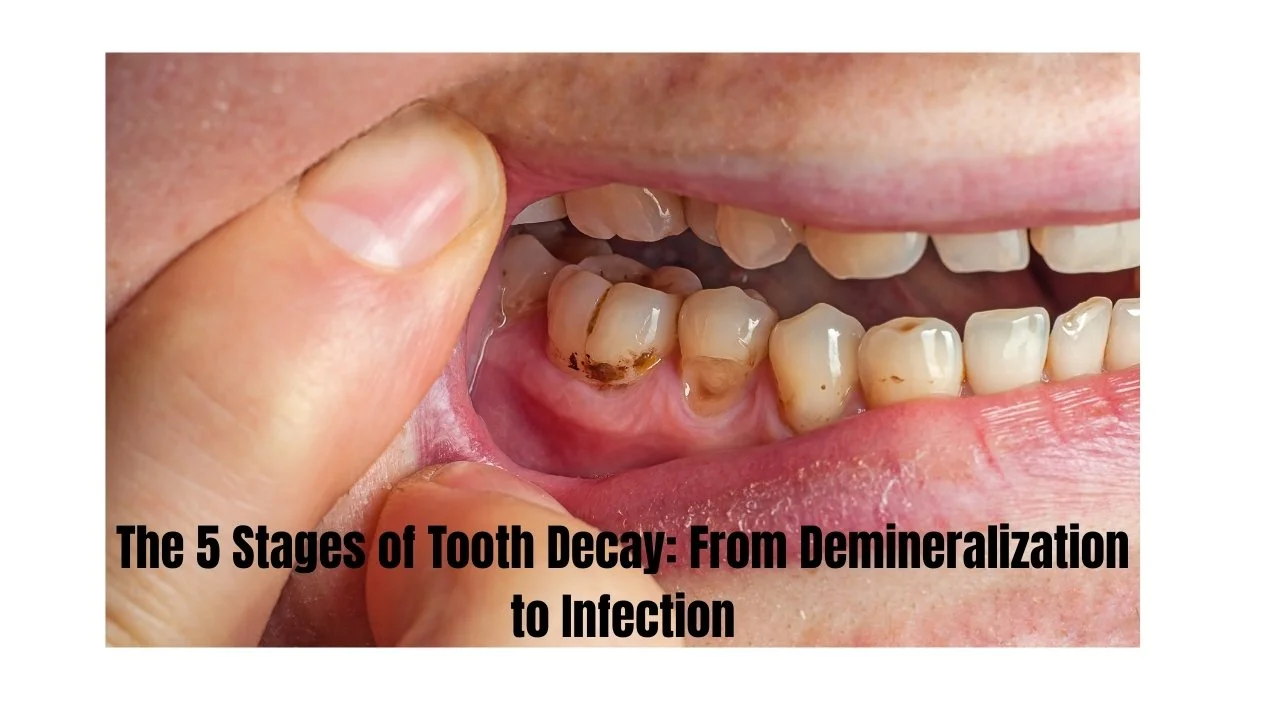
Stage 1: Demineralization
At this initial stage, you might see small white chalky spots of teeth. This occurs by the process of the breakdown of minerals in your tooth enamel. The first stage of tooth decay is in the form of demineralization.
At this point, possibly, you can fill in the hole with some fluoride treatment and improved oral health. The enamel of your teeth is able to heal itself by remineralization.
Stage 2: Enamel Decay
Failure to treat tooth decay will keep on destroying your enamel. Holes (cavities) can be observed.
As soon as decay in the enamel forms a hole, it will be required to be treated by professionals. Flossing and brushing teeth cannot help in repairing holes in your teeth.
Stage 3: Dentin Decay
The tooth is coated by dentin which is the second layer. It’s much softer than enamel. Plaque and bacteria reach this layer faster and, as a result, cavities will develop.
Tooth sensitivity may be observed at this point. Your teeth spots can become dark brown. You will require fillings of teeth or some other dental restoration to seal the cavity.
Stage 4: Pulp Damage
The innermost tooth layer is the tooth pulp. It has pulp which contains nerve and blood vessels of teeth which make your tooth alive. Cavities that get to your pulp may cause you great pain.
One might experience redness and swelling of gums near the tooth. At this point, you will probably have to be subjected to root canal treatment.
Stage 5: Abscessed Tooth
When left unattended, a deep cavity may get infected. This forms a pocket of pus referred to as periapical abscess at the end of your tooth root.
Symptoms of a tooth abscess include:
- Pain that spreads to your jaw or face
- Facial swelling
- Swollen lymph nodes in your neck
- Fever
Tooth abscess may be transferred to the other tissues and other body parts. Sepsis In uncommon instances, it might infect your brain or blood.
What Causes Cavities? Understanding the Root of Tooth Decay
The Cavity Formation Process
Cavities form through a specific process:
Mouth bacteria are nutrients that feed on starchy and sweet items.
These bacteria break down carbohydrates to acids.
Dental plaque is made by mixing bacterial, acidic, food, and saliva.
This is a plaque which sticks to your teeth.
Tooth enamel is dissolved by acids of the plaque without adequate cleaning.
This provides holes or cavities in your teeth.
Dietary Factors Contributing to Cavities
Certain foods and drinks increase your risk of cavities:
High-risk foods and beverages:
Food and beverages with high levels of sugar such as candy, soft drinks, and juice.
Bread, cereal, and crackers are considered as starchy food.
Chewable substances that adhesively stick to the teeth.
Natural sugar drinks such as milk.
Eating in between meals also makes you risky. When you take something sweet or starchy to eat or drink, the bacteria in your mouth make acid during the next 20 minutes.
Lifestyle Risk Factors for Tooth Decay
Several lifestyle factors can increase your cavity risk:
Unhealthy mouth – failure to brush teeth or floss on a regular basis.
Medication induced or medical induced dry mouth.
Regular between meal snacks.
Not getting enough fluoride
Failure to visit your dentist to have regular dental checkups.
Cavity Diagnosis: How Dentists Detect Tooth Decay
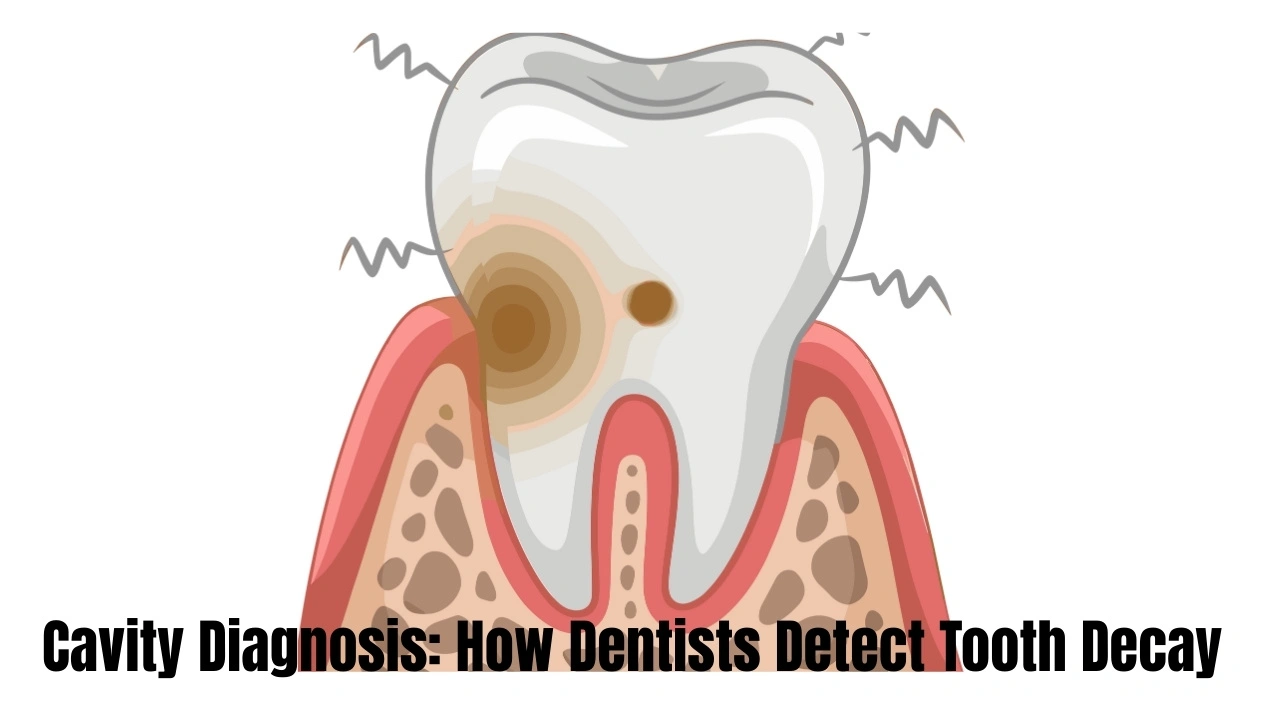
Professional Cavity Detection Methods
Cavities should be detected at an early stage and this is best done through dental checkups twice a year. There are a number of ways that your dentist can detect tooth decay:
Dentist examination includes:
Moral examination of your teeth.
Probing of teeth to determine the presence of soft spots.
Sensation of regions of broken enamel.
It is possible to detect cavities in the dental X-rays even though they cannot be seen with the naked eye. X-rays assist your dentist to view the decay among teeth and underneath the already existing dental fillings.
At-Home Cavity Recognition
White chalky spots on teeth
Brown or black spots on teeth
Sensitive to hot, cold or sweet tooth.
Toothache or mouth pain
Villainous stench like an albatross.
What does your dentist expect you to call? Call your dentist in case you realize any of these signs or in the event that it has taken more than six months since you had a checkup.
Cavity Treatment Options: Fixing Tooth Decay
Early-Stage Cavity Treatments
Enamel damage can be fixed with the help of fluoride treatment in extremely young ages in case of tooth decay. This is referred to as remineralization. It has the ability to reverse early cavities.
Fluoride treatment options include:
- Toothpaste and mouthwash- prescription.
Treatment of fluoride at the dentist.
Greater levels of strength in fluoride use.
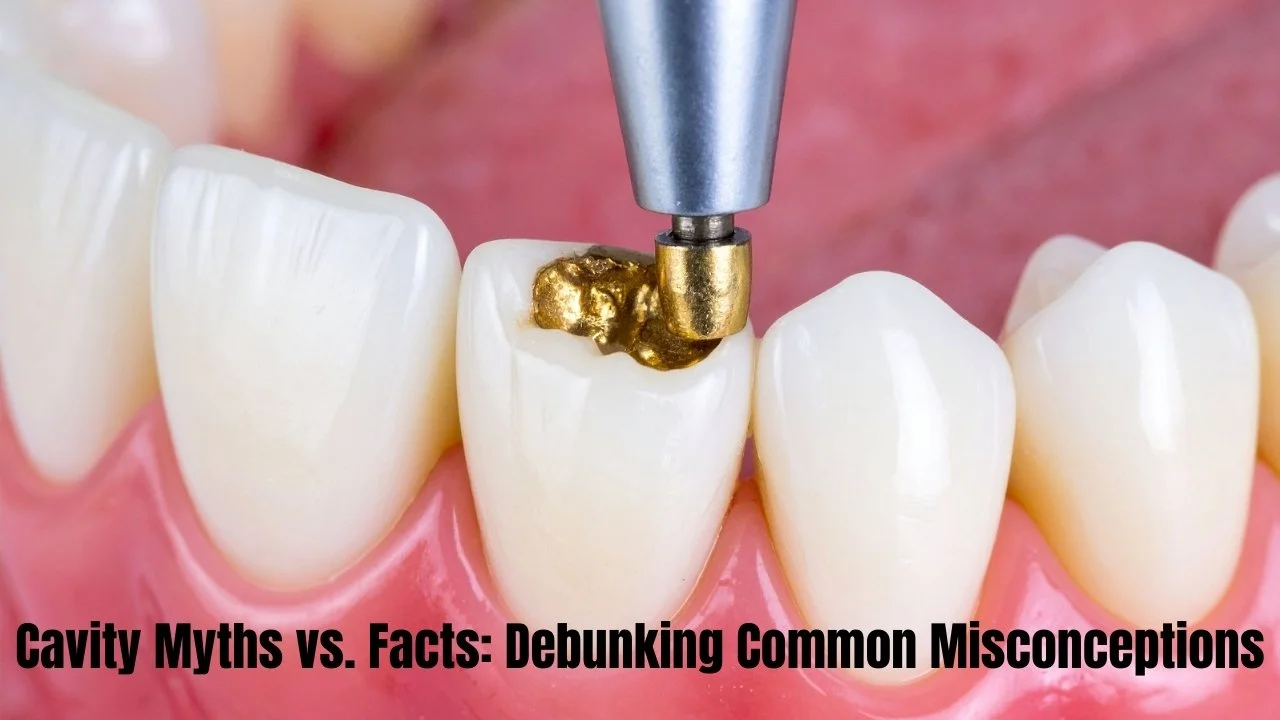
Standard Cavity Fillings
Once a hole forms in your tooth, your dentist drills out the decayed tissue and fills the hole. Dental fillings come in different materials:
- Composite resin (tooth-colored material)
- Silver amalgam (metal filling)
- Gold fillings (less common)
Composite resin fillings are popular because they match your tooth color. They work well for small to medium cavities.
Advanced Cavity Treatments
For severe tooth decay, you may need more advanced treatments:
Root canal treatment alleviates the pain of the severe decay of the teeth. This procedure is normally conducted by an endodontist (specialist). In endodontics, the dentist endodontist removes the tooth pulp and the pulp chamber is filled with gutta-percha.
Dental crown may also be required to strengthen the tooth that is being treated. Weakened teeth are covered with dental crowns.
Root canal therapy might not be possible; therefore, tooth extraction might be required. Dental implant or dental bridge may be required to replace a tooth which is extracted.
Cavity Prevention: Stopping Tooth Decay Before It Starts
Essential Oral Hygiene for Cavity Prevention
Good oral hygiene is your best defense against cavities:
Brushing teeth properly:
- Use a soft–bristled toothbrush
- Use fluoride toothpaste
- Brush at least twice daily, preferably after every meal
- Brush for two minutes each time
Flossing daily removes plaque and food particles between teeth. Areas between teeth are common spots for cavities to form.
Dietary Changes to Prevent Cavities
Reducing sugary and starchy foods helps prevent cavities:
- Limit sugary foods and drinks
- Choose water over sugary beverages
- Eat sugary or starchy foods with meals, not as snacks
- Rinse with water after eating sweet or sticky foods
Cavity-fighting foods include:
- Cheese and other dairy products
- Leafy greens
- Almonds and other nuts
- Foods high in fiber
Professional Preventive Care
The frequent dental checkups can detect cavities at an early stage. The vast majority of the population must pay their dentist twice per year. A higher number of visits might be necessary in case you are prone to tooth decay.
Back teeth Chewing surfaces of your back teeth are covered by dental sealants. Sealants are thin plastic layers that ensure that the food and bacteria do not stick in the crevices of your teeth.
Professional fluoride varnish makes your tooth hard which gives you a chance to avoid dental cavities.
Living with Cavities: Management and Long-term Outlook
Cavity Recovery and Aftercare
After cavity treatment, follow your dentist’s instructions:
- Avoid hard or sticky foods for 24 hours after dental fillings
- Take over-the-counter pain medicine if needed
- Call your dentist if you have severe pain or swelling
- Keep up with good oral hygiene
Tooth sensitivity after treatment is normal and usually goes away in a few days.
Preventing Future Cavities
Once you’ve had cavities, you’re at higher risk for getting more. Prevent future tooth decay by:
- Maintaining excellent oral hygiene
- Using fluoride toothpaste and mouthwash
- Limiting sugary and starchy foods
- Getting regular dental checkups
- Following your dentist’s specific recommendations
When to See a Dentist for Cavity Treatment
Emergency Cavity Symptoms
Call your dentist right away if you have:
- Severe toothache or mouth pain
- Facial swelling
- Signs of infection like fever
- Bleeding gums with pain
- Tooth sensitivity that’s getting worse
These symptoms may mean you have an advanced cavity or tooth abscess that needs immediate treatment.
Routine vs. Urgent Dental Care
The frequent dental check-ups should be done after every six months to identify the cavities early. Treatment is easier, cheaper and more comfortable at an early stage.
There is no need to visit your dentist after they cause pain. There are numerous cavity types that do not make them painful at an early stage. You can also require more extensive treatment before a cavity is painful.
Cavity Myths vs. Facts: Debunking Common Misconceptions
Can Cavities Heal Naturally?
Fact: Very early cavities can sometimes reverse through remineralization. Your tooth enamel can repair itself if the cavity only affects the surface.
Myth: All cavities will heal on their own. Once decay reaches the dentin layer, you need professional treatment. Dental fillings or other dental restoration are necessary to fix established cavities.
Cavity Contagion Concerns
Fact: The bacteria that cause cavities can pass from person to person through saliva. Kissing, sharing utensils, or sharing drinks can spread these bacteria.
Myth: You can “catch” a cavity like a cold. You can’t directly catch a cavity, but you can pick up bacteria that increase your risk of tooth decay.
Cavity Costs and Insurance: Financial Aspects of Tooth Decay Treatment
Treatment Cost Breakdown
Cavity treatment costs vary by type and location:
- Dental fillings: $50-$300 per tooth
- Root canal therapy: $500-$1,500 per tooth
- Dental crowns: $800-$1,500 per tooth
- Tooth extraction: $75-$300 per tooth
Prevention costs much less than treatment. Regular dental checkups and good oral hygiene save money in the long run.
Insurance Coverage for Cavity Treatment
Most dental insurance covers:
100 percent of preventive services such as dental checkups and cleanings.
Eighty percent of simple interventions such as dental fillings.
50% of them such as root canal treatment and dental crowns which are major treatments.
Check with your insurance company about your specific coverage. Some plans have waiting periods for major treatments.
Conclusion
Cavities are prevalent, although they can be avoided. Knowledge of the development of tooth decay makes you take care of your teeth. The best preventive measures to cavities are good oral health, reduced intake of sugary foods and beverages, and regular dental checkups. If you need info related What Date Is 90 Days From Today.
Remember these key points:
Use fluoride toothpaste in cleaning teeth twice in a day.
Brush every day to get the foreign matter in between the teeth.
Restrict the intake of sugary and starchy food.
Visit your dentist after every six months.
Vigilante signs of tooth decay.
It is simpler and cheaper to treat cavities at an earlier stage rather than when pain occurs. Call your dentist now in case you believe you have a cavity. By taking care of your teeth you are ensuring that you have a healthy smile in the coming years.
The dentist can develop an individual treatment to avoid cavities and take care of your mouth. Loss of teeth is something that you should not allow to ruin your life. If well maintained and with assistance of a professional, your teeth will remain healthy and cavity-free.
Additional Resources
Recommended Oral Care Products
Toothpaste with ADA certification seal.
Soft bristled toothbrush or electric toothbrush.
Fluoride mouthwash to be used as an added safety measure.
Toilet tissues or water sprinklers.
Cavity Prevention Checklist
[ ] Floss daily
[ ] Restrict sugary and starchy food.
[ ] Having dental checkups after every six months.
[ ] Take back teeth dental sealants.
[ ] Take fluoride mouthwash on recommendation.
Contact your dentist if you experience:
Toothache or mouth pain
Sensitivity of the teeth to hot, cold or sweet.
Spots on teeth white, brown or black.
Defective breath that will not be resolved through brushing.
The concerns about your oral health.